LIMS Implementation Project Plan: Strategies for a Flawless Rollout
Considering a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) for your lab?
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know—from defining clear lab objectives to overcoming implementation challenges.
LIMS Implementation Project Plan
Here’s a detailed step-by-step project plan for your LIMS implementation. This comprehensive plan ensures a structured approach to the implementation.
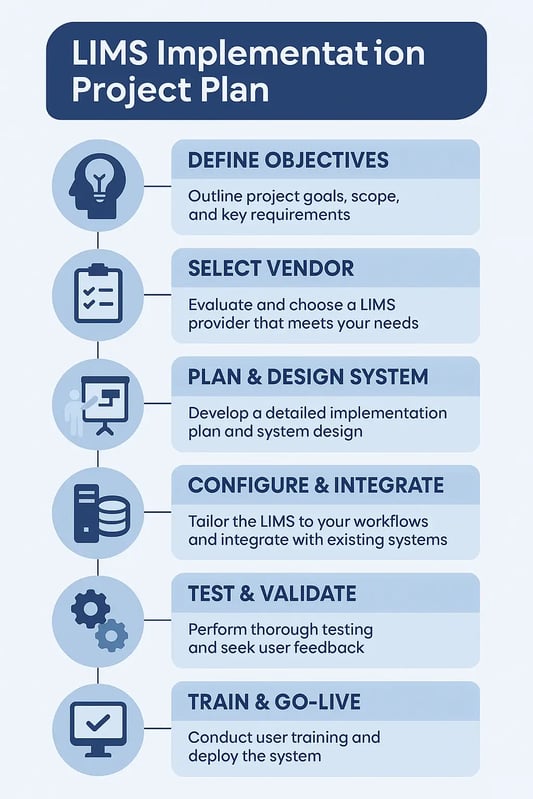
Understanding LIMS Software Implementation Process

Laboratory Information Management Systems is pivotal in managing laboratory data and automating workflows to enhance laboratory efficiency.
The fundamental reason for introducing a LIMS into laboratory operations is its capability to manage copious amounts of lab information effectively, thereby optimizing the workflow within laboratories.
In today’s era, where modern laboratories are witnessing an unprecedented surge in data volume, employing a LIMS becomes essential for organized lab data management and improved efficiency .
The utility of a LIMS spans numerous aspects of laboratory processes including...
-
Protocol execution
-
Sample tracking data
-
Workflow facilitation
-
Maintaining quality control measures
By curtailing manual inputting practices significantly through automation with a LIMS deployment, as outlined in the user requirements document, can lead to greater precision and reliability in the generated datasets. A LIMS minimizes human error, thus enhancing data accessibility to lab managers and workers.
Offering that facilitates immediate access to data from any location at any time, Enhances quick decision-making abilities along with augmenting operational responsiveness.

Cloud-based LIMS solutions must address potential cloud based data compromises while allowing instant access to data from anywhere, anytime, enabling faster decision-making and improved operational responsiveness.
These systems go beyond organizing information—they enhance overall lab efficiency while reducing costs tied to routine operations, ensuring careful planning in the implementation . Implementing a LIMS can save laboratories time and money by streamlining workflows.
Key Steps in the LIMS Implementation Process
Implementing a LIMS system may seem complex, but a clear, agile approach that includes document configuration requirements can simplify the process. Instead of relying on a traditional method, this flexible approach focuses on continuous planning, feedback, and gradual improvements, ensuring the system evolves to meet your lab's changing needs.
Step #1 - Defining Your Lab Objectives
Step #2 - Choosing the right LIMS vendor
Step #3 - Plan & Design LIMS System
Step #4 - Configure & Integrate
By using this agile method, labs can achieve quicker deployments, better user adoption, and a system that grows and adapts with their operational needs.
Step #1 – Defining Your Lab Objectives
Begin by setting clear, measurable objectives that align with your lab’s operational and strategic goals. These will serve as the foundation for every decision during implementation. Defining goals for the new system provides a clear understanding of its purpose.
Consider:
-
Business and compliance requirements
-
User needs across departments
-
Current IT infrastructure and integration needs
-
Data handling, reporting, and audit trail expectations
Use agile planning to break objectives into manageable phases. This allows the system to evolve gradually and ensures early feedback informs later decisions. Clear goals ensure a more efficient implementation and a system built for long-term success.
Step #2 – Choosing the Right LIMS Vendor
The vendor you choose plays a pivotal role in the project’s success. Look for LIMS providers with:
-
A proven track record in your industry
-
Scalable, customizable solutions
-
Subscription-based or agile pricing models
-
Strong onboarding and ongoing support
The legal and scientific content within contracts should be properly reviewed before finalizing LIMS procurement.
Avoid vendors offering bloated systems or rigid solutions that don’t adapt well to your workflows. Your ideal partner should prioritize continuous value delivery and user-centered design. A flexible vendor aligned with your goals makes for a more successful, future-ready deployment, especially when considering the implementation costs . Choosing a configurable LIMS can help avoid high customization costs.
Step #3 – Plan & Design LIMS System
With objectives and a vendor in place, map out the system design in detail. Create a phased project plan that includes:
-
Workflow diagrams
-
Data structure requirements
-
Key milestones for each sprint
A thorough LIMS implementation plan must outline timelines, performance metrics, and vendor choices. Collaborate closely with the implementation team to align design choices with your lab’s needs. Focus on high-priority features first using a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) approach. This keeps the project agile, efficient, and responsive to real user input. Laboratories need to specify all requirements for their LIMS after signing contracts.
Step #4 – Configure & Integrate
Now it's time to bring your design to life. Work closely with your implementation partner to:
-
Configure sample tracking, reporting, and integration with lab instruments
-
Align workflows with the system’s logic
-
Set up user roles, permissions, and dashboards
Ensure security protocols and data governance are built into every step. Plan for seamless data migration by validating legacy datasets before importing. Taking a modular, agile approach to configuration allows for phased feature rollouts and reduces disruption during go-live.
Step #5 – Test & Validate
Testing is critical to ensure everything works as expected. Conduct iterative testing throughout the process, not just at the end. Focus areas include:
-
Functional testing of workflows
-
Integration testing with external systems
-
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) with real end users
Avoid the mistake of excluding daily users from UAT during the testing process . Their feedback is essential to refining the system for real-world use. Test at the end of each sprint and address feedback immediately—this strengthens system usability and sets the stage for smooth adoption.
Step #6 – Train & Go-Live
Training and support are the final steps before full deployment.
Tailor training sessions to different roles:
-
Lab technicians: daily usage
-
Managers: reporting and oversight
-
IT teams: maintenance and troubleshooting
Training should adopt a 'Train the Trainer' approach for effective knowledge transfer.
Provide hands-on experience and access to learning resources. Once training is complete, launch the system with a strong support structure in place—dedicated contacts, helpdesk access, and regular progress updates. Monitor closely during the first weeks and continue improving based on user feedback.
Overcoming LIMS Implementation Challenges
Implementing a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) brings numerous benefits but can also pose challenges, such as resistance to change, regulatory compliance demands, and avoiding unnecessary complexity.

A common issue arises when users try to mold the software to fit existing business processes, rather than adapting workflows to align with the technology.
Embracing process changes that the software enables often leads to better outcomes and is essential for maximizing returns on investment.
Creating a dedicated management team and fostering a culture open to revising standard operating procedures can help laboratories overcome these obstacles.
By being receptive to process improvements driven by the LIMS, users can enhance efficiency and achieve greater satisfaction with the system.
Managing Change in Laboratory Workflows
Implementing a new software system can be particularly challenging due to the alterations required in existing laboratory workflows. Laboratories typically have a deep-rooted reliance on traditional systems like spreadsheets, which complicates the shift to new practices. There must be an openness towards modifying these lab routines to harness enhanced efficiency through the novel LIMS setup.
It falls upon lab managers not only to delineate the advantages of integrating a new LIMS but also actively involve all members of laboratory personnel during this transitionary phase. This inclusive approach helps reduce resistance and promotes the seamless adoption of updated workflows.
By ensuring that this fresh system aligns with overarching lab goals and securing participation from every stakeholder, one can facilitate an easier changeover while boosting operational efficacy.
Agile methodologies are particularly effective in overcoming resistance to change, especially as the business environment evolves . By involving users in regular feedback cycles and incorporating their insights into each sprint, labs can foster a sense of ownership and reduce adoption barriers.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a cornerstone of LIMS implementation, addressing standards such as FDA 21 CFR Part 11, GLP (Good Laboratory Practices), and ISO 17025.
Maintaining robust data security throughout the transition phase is critical, ensuring sensitive information like client details, health records, and medication history is securely managed in adherence to these guidelines.
Verification processes must track representative samples through their entire workflow to confirm that every aspect of the system integration functions as required. Regular internal audits and external reviews are also essential to ensure ongoing compliance with regulatory requirements and system dependability over time.
By rigorously validating and consistently verifying LIMS implementations during the actual implementation , laboratories can demonstrate adherence to industry-specific regulations, safeguard data integrity, and confidently meet global standards.
Avoiding Overcomplication
The LIMS implementation process can easily become overly complex if the focus shifts away from core functionalities and primary objectives. To avoid unnecessary complications, it’s essential to prioritize the lab’s critical needs.
Thorough preparation and a clear understanding of your lab’s requirements are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and ensuring a streamlined, effective system.
Post-Implementation Best Practices
After implementing a LIMS, the focus should shift to increasing user adoption to maximize its impact.
Regularly evaluating functionality and data quality, providing ongoing training and support, and gathering user feedback are key to improving system usage and user engagement.

These steps ensure the LIMS continues to meet the needs of the lab while fostering confidence and efficiency among users.
By prioritizing these strategies, laboratories can ensure that the LIMS software is fully embraced by users, unlocking its full potential and sustaining long-term operational success.
Regular System Updates
The LIMS implementation process includes several stages, and laboratories must revisit steps three to seven when integrating new features. This approach ensures the system stays up to date with the latest security updates and functional improvements, aligning with evolving lab needs and industry regulations.
Regularly incorporating new releases and enhancements allows labs to take advantage of technological advancements, improving operational efficiency. By staying current, the LIMS continues to be a valuable tool for streamlining laboratory operations and maximizing productivity.
Continuous Training and Support
Continuous training and assistance are crucial for leveraging the full potential of the LIMS system. Comprehensive training prepares users to tackle any emerging issues or glitches with confidence. By including laboratory staff in user acceptance testing, it’s possible to pinpoint specific functions or processes that may require additional tweaking. Involving lab personnel early on helps reduce opposition to new methods and promotes seamless integration.
It is vital that User Acceptance Testing (UAT) be performed to confirm that all users receive adequate instruction on how to utilize the laboratory system effectively. Training a wide range of users during this stage enhances both reliability and security of the solution.
Persistent training efforts alongside ongoing support keep end-users up-to-date regarding fresh upgrades and capabilities, guaranteeing that the LIMS system remains well-suited for fulfilling evolving requirements within the laboratory environment.
Monitoring and Feedback
Continuous surveillance and constructive responses are vital to sustain the LIMS system’s effectiveness. Once laboratory operations begin utilizing the system, assessing it against predefined test cases and goals aids in pinpointing potential enhancements. Candid feedback from users, provided promptly, is essential for refining the LIMS post-deployment.
Systematic appraisals of additional functionalities and improvements, including data structures, guarantee that the LIMS progresses in alignment with the laboratory’s changing requirements.
Collaboration with vendors during updates is key to successfully embedding new features while swiftly resolving any complications that arise.
Persistent oversight paired with insightful feedback secures LIMS's role as an invaluable asset for adept project management skills outside of laboratory processes.
Snic Solutions - The LIMS Vendor That Understands Your Lab
Implementing a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) is a complex undertaking that requires the right partner—one who understands the demands of compliance, efficiency, and change management.
As a trusted LIMS vendor of Opcenter RD&L, Snic Solutions offers full-service implementation designed around your lab’s unique workflows, systems, and strategic goals. Our team of experienced engineers and project managers collaborates closely with your team to deliver a fully configurable LIMS solution—on time and on budget.
Built for flexibility and compliance, our cloud-based LIMS platform supports:
-
Seamless integration with lab instruments and enterprise systems
-
Robust data security and traceability aligned with FDA, GLP, and ISO standards
-
Agile deployment cycles that encourage continuous feedback and faster ROI
Whether you're replacing spreadsheets or scaling a multi-site operation, Snic Solutions ensures your LIMS implementation drives real results—empowering your lab to operate smarter, faster, and with greater confidence.
Summary
To wrap it up, achieving a successful launch of a LIMS requires meticulous preparation, choosing an appropriate supplier, precise system setup, securing data protection, and executing comprehensive user acceptance testing. Tackling typical obstacles and adhering to best practices after deployment is crucial for sustaining the advantages brought by the LIMS.
By following these directives faithfully, labs can enhance efficiency significantly, elevate their manufacturing data management capabilities,and boost their general output levels.
By applying agile methodologies throughout the implementation process, laboratories can achieve a system that not only meets their current needs but evolves alongside future challenges. This approach ensures greater adaptability, faster results, and sustained user engagement.
Other Software Implementation Guides
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key steps in the LIMS implementation process?
The key steps in the LIMS implementation process are defining lab objectives, selecting the appropriate LIMS software verification vendor, configuring the system, ensuring data security, and performing user acceptance testing.
Following these steps will help ensure a successful implementation.
How can we ensure data security during LIMS implementation?
It is imperative to establish rigorous security protocols and formulate an extensive strategy for the shift towards the new system in order to maintain data security throughout the implementation of LIMS.
It is vital to safeguard data housed in cloud-based environments against possible incursions.
Why is User Acceptance Testing (UAT) important?
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) is essential as it ensures the system fulfills user needs and functions appropriately, while also enabling the discovery of possible improvements through user feedback.
The outcome of this procedure results in enhanced functionality and heightened satisfaction among users.
What are some post-implementation best practices for LIMS?
To ensure the ongoing effectiveness of your LIMS, implement regular system updates, provide continuous training and support, and establish a feedback mechanism for monitoring performance.
These practices will maximize the benefits of the system over time.
How does LIMS differ in discrete vs process ecosystems?
LIMS focuses on tracking and testing individual components or batches in discrete ecosystems, emphasizing unit-level traceability and defect detection, often integrated with MES systems. LIMS is tailored for managing continuous or batch processes in process ecosystems, ensuring consistency, regulatory compliance, and monitoring across raw materials, in-process, and finished goods.
The key distinction lies in their focus: discrete ecosystems prioritize part-level traceability, while process ecosystems emphasize bulk product quality and process control.
What's the difference between LIMS, research and development, and laboratory execution software?
LIMS manages sample tracking, data workflows, and compliance for routine lab operations. Research and Development (R&D) software supports early-stage experimental data, ideation, and innovation processes for product development.
Laboratory Execution Systems (LES) guide and enforce step-by-step lab procedures, ensuring process adherence and real-time documentation of experimental or operational activities.
Share this
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

LIMS Software for Small Laboratories

Top Strategies for Effective Laboratory Operations Management



No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think