What is Industry 4.0 & the 4th Industrial Revolution
Industry 4.0 and the Fourth Industrial Revolution refer to the latest industrial revolution phase, characterized by smart manufacturing and the fusion of advanced technologies that blur the lines between the physical, digital, and biological worlds. This era of smart technology is driven by innovations such as the industrial Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), big data, robotics, and advanced manufacturing techniques.
The Evolution of Industrial Revolutions
The journey from steam engines to smart factories to cloud computing is a captivating narrative of human ingenuity and progress. Each industrial revolution has propelled us forward, pushing the boundaries of what is possible and reshaping the world as we know it. Reflecting on the previous industrial revolutions highlights the progression and profound impact leading up to the Fourth Industrial Revolution, which builds on the digital revolution of the third industrial era with unprecedented velocity, scope, and systems impact.
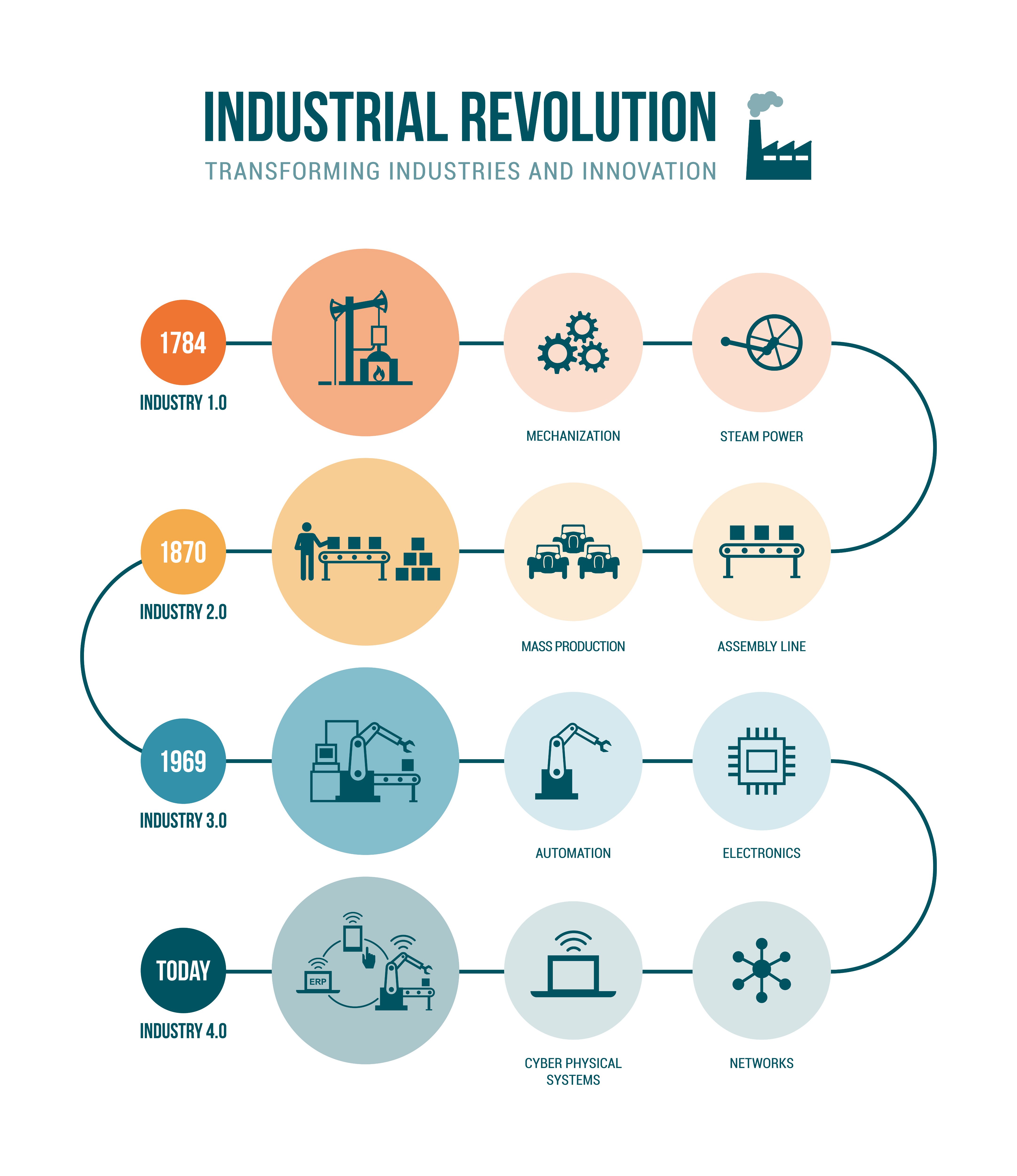
The First Industrial Revolution
Time Period: 1765-1870
The First Industrial Revolution introduced mechanization, harnessing the power of water and steam to drive the wheels of industry. It was a time of innovation and transformation, as manual labor gave way to machine power, revolutionizing production processes and labor markets, paving the way for unprecedented economic growth.
The Second Industrial Revolution
Time Period: 1870-1969
The Second Industrial Revolution brought with it the advent of electricity, further propelling mass production and transforming industries on a global scale. This era saw the rise of factories and assembly lines, enabling the production of goods on an unprecedented scale. It was a time of efficiency and progress, as technology continued to shape the world around us.
The Third Industrial Revolution
Time Period: 1969-2000
The digital era marked the Third Industrial Revolution, characterized by the digital revolution and the widespread adoption of computers and the internet. This era brought about a new level of connectivity and global communication, revolutionizing the way we live, work, and interact with the world. It was a time of information and technological innovation everywhere, as the digital realm became an integral part of our daily lives.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution
Time Period: 2000-current
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is where the fusion of technologies is blurring the lines between the physical, digital, and biological spheres, characterized by the use of automation, advanced data analytics, and smart and autonomous systems. It is an era marked by the Internet of Things (IoT), big data and analytics, and the integration of the physical worlds and digital systems.
A key element of this revolution is the smart factory, where cyber-physical systems monitor the physical processes of the factory and make decentralized decisions, showcasing the integration steam power of robotics, automation, and machine-learning algorithms within manufacturing facilities. This revolution is transforming industries once again, leading us toward a future of smart factories, personalized medicine, and intelligent machines.
What are the Current Pillars of Industry 4.0?
Cyber-Physical Systems

Cyber-physical systems are central to Industry 4.0, bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds. These systems integrate the physical production processes with computer-based algorithms, enabling machines to become intelligent and autonomous. Examples include Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS), and Supply Chain Planning (SCP). These interconnected systems communicate with each other and with machines, creating a network of devices and processes. This integration allows for real-time monitoring, analysis, and decision-making, enhancing efficiency, productivity, and flexibility in all manufacturing processes.
Internet of Things (IoT)

IoT revolutionizes connectivity in Industry 4.0 by enabling seamless data exchange between devices, machines, and humans. In smart factories, IoT enables real-time monitoring and intelligent decision-making. For example, sensors in machines collect performance data, allowing for predictive maintenance and reduced downtime. IoT extends beyond manufacturing, impacting healthcare, transportation, and logistics. In healthcare, IoT enables remote patient monitoring and for smart machines and medication dispensers. In logistics, IoT optimizes routes, monitors fuel consumption, and tracks deliveries, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Big Data and Analytics

In Industry 4.0 data is an asset. Big data and analytics allows you to unlock the value in all that data for insights and decision making. Analyse production data to optimise workflows, reduce waste and increase productivity. Analyse customer data to tailor products and marketing to customer needs. In supply chain management real time data from suppliers, logistics partners and customers gives visibility and decision making, reduces lead times and improves inventory management.
Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics is changing manufacturing by making it more efficient and precise. Robotic arms and conveyor belts do repetitive tasks fast and accurate, reduces human error and increases productivity. Automation systems allows continuous production, maximise output. AI and machine learning allows robots to adapt to changing conditions. Advanced sensors and algorithms makes automation more beneficial in industries that requires high accuracy such as electronics and pharmaceuticals.
Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
AI and machine learning (ML) is the drivers of predictive maintenance, quality control and optimisation in Industry 4.0. AI algorithms analyse historical data to predict equipment failures so proactive maintenance can be done. In quality control AI detects deviations from standards so immediate corrective action can be taken. AI and ML also enhance supply chain management by predicting demand, optimise inventory and identify the most efficient transportation route, resulting to cost savings and improved manufacturing efficiency.
Figure: Use Cases of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Manufacturing
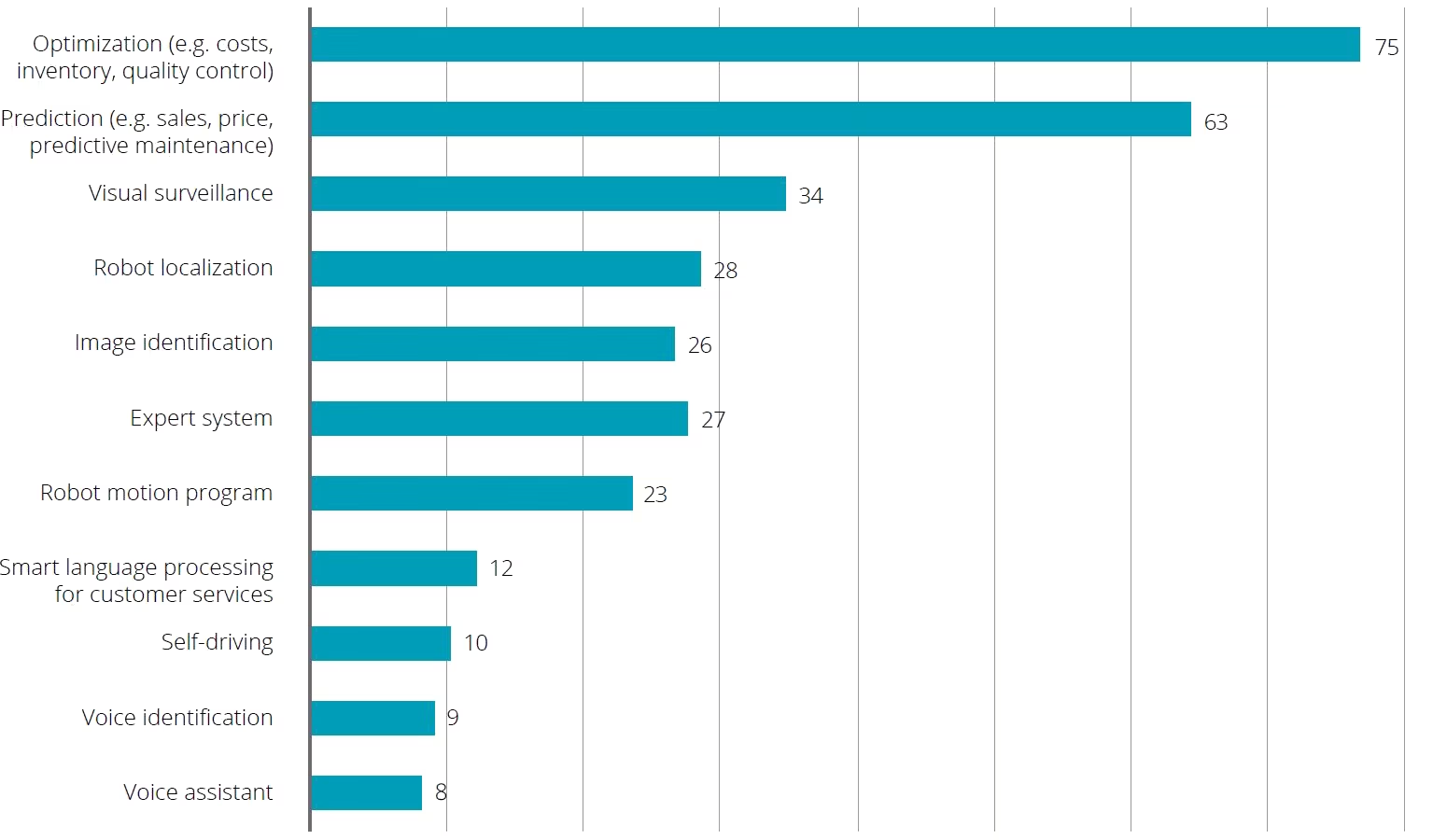
Source: 2019 Deloitte survey on AI adoption in manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)

Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, offers unprecedented customization and flexibility in the manufacturing process. It allows the creation of complex designs and intricate details that traditional methods cannot achieve. 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, reducing time to market and development costs. It supports on-demand manufacturing, allowing businesses to produce small batches and quickly respond to customer demands. Additionally, 3D printing minimizes material waste, promoting sustainability and cost-efficiency.
Industry 4.0 is Transforming Multiple Industries
Industry 4.0 isn't limited to manufacturing; its impact is revolutionizing various sectors of entire economy, unlocking new possibilities and transforming business operations across the board.

Healthcare: Patient Centric Care
In healthcare Industry 4.0 is enabling patient centric care. By combining artificial intelligence and data analytics healthcare providers can collect and analyse vast amounts of patient data. This allows them to leverage data to create treatment plans and improve outcomes, improve patient care and reduce costs and improve overall efficiency in the healthcare system.
Agriculture: Precision Farming
In agriculture Industry 4.0 is changing crop cultivation and harvesting. Precision farming techniques enabled by sensors and data analytics allow farmers to monitor and analyse soil conditions, weather patterns and crop growth in real time. With this data farmers can optimise irrigation, fertilisation and pest control, resulting in better yields and reduced environmental impact. This means more productivity and profit for farmers and food security and sustainability for the growing global population.
Transportation: Autonomous Vehicles and Connected Logistics
Industry 4.0 is making big progress in the transportation and communication costs. Autonomous vehicles and connected infrastructure is changing transportation for people and goods. Self driving cars can reduce traffic congestion, improve road safety and overall transportation efficiency. Connected logistics allows real time tracking and optimisation of global supply chains so goods get to customers faster and more reliably. This means customer satisfaction and reduced costs and environmental impact of transportation.
Energy: Smart Grids and Renewable Integration
In energy Industry 4.0 is driving the adoption of renewable energy and energy efficiency. Smart grids enabled by sensors and communication technologies allow real time monitoring and control of energy generation, distribution and consumption. This means more efficient use of energy resources, less fossil fuels and renewable energy integration into the grid. So the energy sector becomes more sustainable, resilient and able to meet future energy demands.
By adopting Industry 4.0 technologies these sectors are not only becoming more efficient and productive but also more sustainable and innovative. The Industry 4.0 transformation is paving the way for a future where industries are more intelligent and effective for the benefit of society and the whole economy.
The Challenges and Risks of the Fourth Industrial Revolution
With great change comes great challenge. Industry 4.0 brings new technologies but also new risks and challenges to be addressed.
Cyber Security
In a world of digital everything cybersecurity is top of mind. The interconnectivity of devices and computer systems means more risk of data breaches and cyber attacks. Businesses must invest in advanced cybersecurity technologies and protocols to secure their operations and protect their data from unauthorised access. Strong cybersecurity is essential to mitigate the risks of the Industry 4.0 connected and digital world.
Job Displacement due to Automation
Job displacement due to automation is another big issue. While AI and ML improves efficiency and productivity it can disrupt traditional job roles. As automation replaces manual labour the employment and workforce stability concerns grow. To address this businesses and governments must invest in retraining programs, reskilling initiatives and create new job opportunities that align the job market with the changing technological landscape. Prioritising workforce development can mitigate the negative impact of automation on labour, disrupt labor markets, and maximise the benefits for businesses and employees.
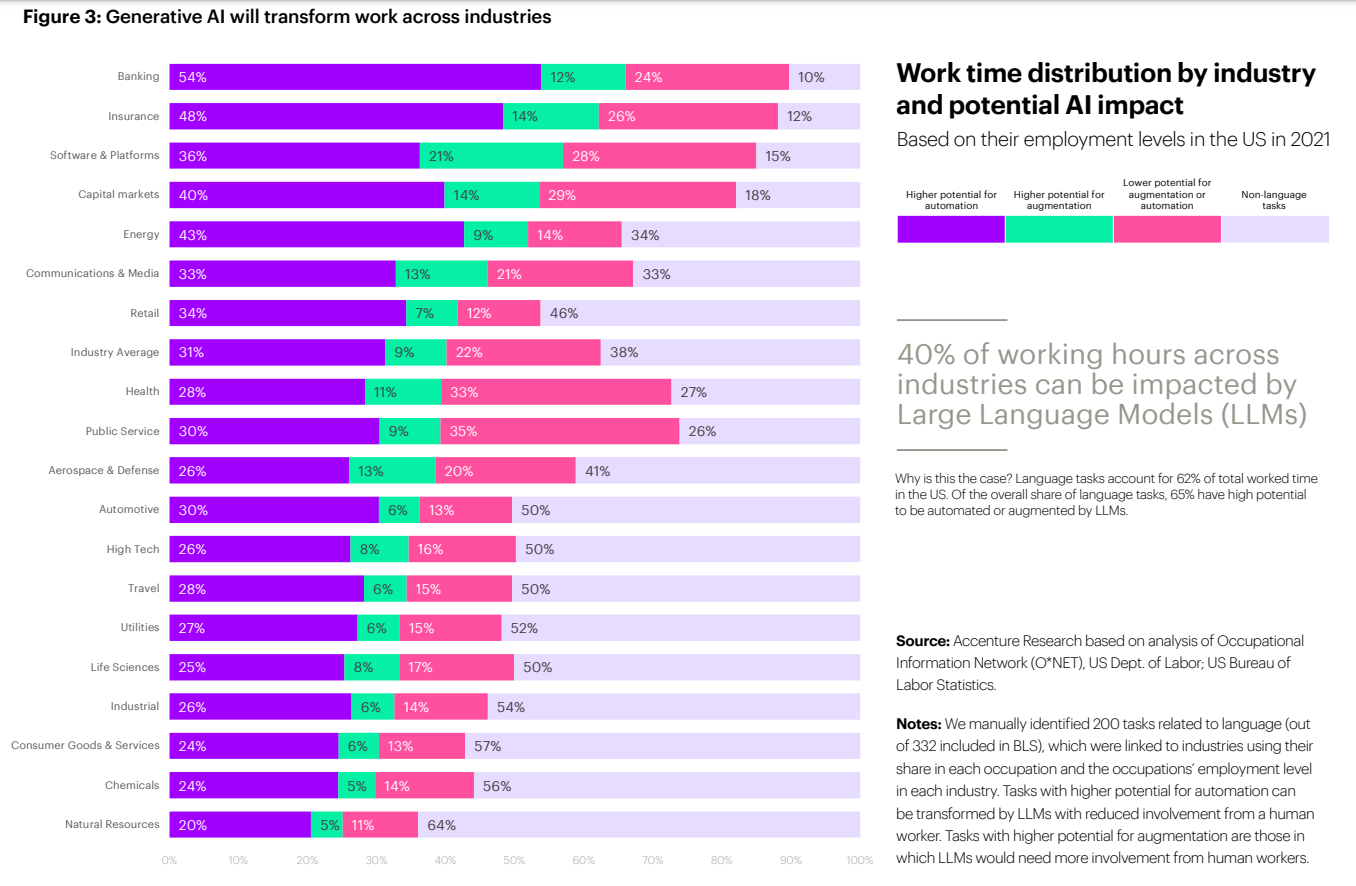
Source: Accenture
AI and Data Privacy
As Industry 4.0 rolls out, AI and data privacy ethics become more critical. Responsible AI means addressing privacy, consent, transparency and control over personal data. Businesses must have robust data protection in place and follow ethical guidelines to protect individuals’ privacy and prevent misuse of personal data.
Bias in AI Algorithms
AI algorithms can mirror the biases in the training data, so algorithms must be fair, unbiased and transparent. This means monitoring and auditing algorithms and ongoing work to address and mitigate any biases that arise.
Employment and Workforce Well-being
The impact of AI on employment raises ethical concerns around job displacement and worker well-being. Automation and AI can lead to job losses, affecting individuals and communities. Businesses and policymakers must invest in workforce development, retraining programmes and new job creation aligned to the technology landscape. This way workers can transition smoothly and the negative effects of automation can be mitigated.
Collaboration and Ethical Frameworks
Addressing these ethical considerations requires ongoing dialogue and collaboration. Businesses, policymakers and society must work together to establish ethical frameworks, guidelines and regulations that promote responsible AI use, protect privacy rights, mitigate biases and put individuals and communities first. By tackling these ethical issues head on we can get the best out of AI and have a fair, inclusive and safe future for all.
The Future of Industry 4.0

As we look to the future, Industry 4.0 is set to continue its transformative journey, ushering in a new era of technological advancements that will redefine the boundaries of what’s possible. The integration of emerging technologies such as quantum computing, nanotechnology, and the Internet of Bodies (IoB) will further revolutionize industries and reshape the way we live and work. Additionally, the World Economic Forum, under the leadership of Klaus Schwab, has been instrumental in recognizing the pioneers of this revolution through initiatives like the Global Lighthouse Network, which collaborates with McKinsey to spotlight organizations and technologies at the forefront of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, providing valuable insights and enablers for successful 4IR transformation.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing promises to exponentially increase computing power and solve complex problems beyond the capabilities of traditional computers. With its ability to process vast amounts of data simultaneously and perform calculations at incredible speeds, quantum computing can revolutionize fields such as drug discovery, cryptography, and logistics optimization. This technology will enable researchers and scientists to tackle some of the most pressing challenges facing humanity and accelerate the pace of scientific discoveries and technological breakthroughs.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology involves manipulating matter at the atomic and molecular scale to create materials and devices with unique properties and functionalities. By harnessing nanoscale engineering, industries can develop advanced materials, sensors, and devices applicable across various sectors. From more efficient and lightweight batteries for electric vehicles to highly sensitive medical diagnostic tools, nanotechnology will enable innovative solutions that enhance performance, sustainability, and quality of life.
Internet of Bodies (IoB)
The Internet of Bodies (IoB) encompasses the integration of technology with the human body through wearable devices, implants, and other bioelectronic technologies. This concept allows individuals to monitor and control their health in real-time, empowering proactive health management and enabling healthcare providers to deliver personalized treatments. The IoB will revolutionize healthcare by enabling early detection and prevention of diseases, enhancing medical interventions, and improving overall health outcomes.
As these emerging technologies evolve and converge, the possibilities for innovation and progress are limitless. The transformative potential of Industry 4.0 will extend beyond our current imagination, shaping a future where technology seamlessly integrates into every aspect of our lives. From personalized medicine and sustainable energy solutions to smart cities and immersive virtual experiences, Industry 4.0 will redefine how we live, work, and interact with the world.
Here is a good infographic from www.futurism.com that showcases what's potentially coming in the future.
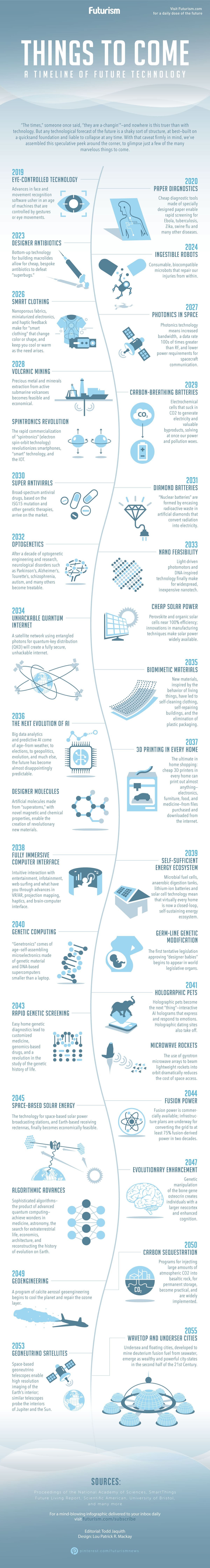
Conclusion
Industry 4.0 isn’t a fad; it’s a fundamental shift in how we interact with digital technology and do business. Keeping up with the pace of change means you’ll understand the opportunities and challenges and can make informed decisions and adjust your strategy. Embracing change, trying new digital technologies and evolving your processes and strategies is key to staying ahead.
As new technologies disrupt old industries and business models thinking outside the box and finding new solutions will be the key to navigating this change. By developing digital skills and a culture of innovation businesses and individuals will be the leaders in their space and will drive economic growth, growth and success in the Industry 4.0 world.
Share this
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

What is Smart Manufacturing?

Industrial-Grade AI: Transforming Operational Efficiency


No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think