Mastering Production Planning KPIs: Key Metrics for Manufacturing Efficiency
Production planning KPIs are vital for optimizing manufacturing efficiency. They help track performance, identify bottlenecks, and streamline operations. In this article, we’ll break down key production planning KPIs and show how they can enhance your production processes for better efficiency and results.
Key Takeaways
-
Production KPIs are essential for tracking manufacturing efficiency, identifying bottlenecks, and aligning production goals with business objectives.
-
Key metrics such as Inventory Turnover Ratio, Cycle Time, and Capacity Utilization are critical for optimizing production processes and enhancing operational efficiency.
-
Leveraging technology for real-time data synchronization and predictive maintenance is vital for effective KPI tracking and improving overall production efficiency.
Understanding Production Planning KPIs
Production KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are essential tools for evaluating how well a manufacturing process is performing. These metrics provide measurable insights that help:
-
Identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies
-
Streamline workflows
-
Support data-driven decision-making
When KPIs are aligned with broader business objectives, they ensure teams focus on the metrics that matter most to operational success—balancing cost, efficiency, and quality.
The Importance of Aligning KPIs with Business Objectives
Business objectives set the strategic direction for production planning. Aligning KPIs with these goals helps manufacturers:
-
Ensure every planning decision supports company-wide priorities
-
Improve resource allocation and scheduling
-
Enhance inventory management and cost control
Benefits of this alignment include:
-
Improved equipment effectiveness and uptime
-
Optimized inventory levels
-
Higher on-time delivery performance
-
Greater customer satisfaction
-
Faster response to market changes
Core Production Planning KPIs
Monitoring the right KPIs provides visibility into efficiency, quality, and resource utilization. These insights allow teams to:
-
Optimize production schedules
-
Evaluate performance across the production line
-
Identify improvement opportunities at every stage
To be effective, KPIs should follow the SMART criteria:
Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Best practices include:
-
Prioritize KPIs that directly impact output and costs
-
Establish baseline values to measure improvement
-
Review and refine KPIs regularly to stay aligned with business needs
Inventory Turnover Ratio
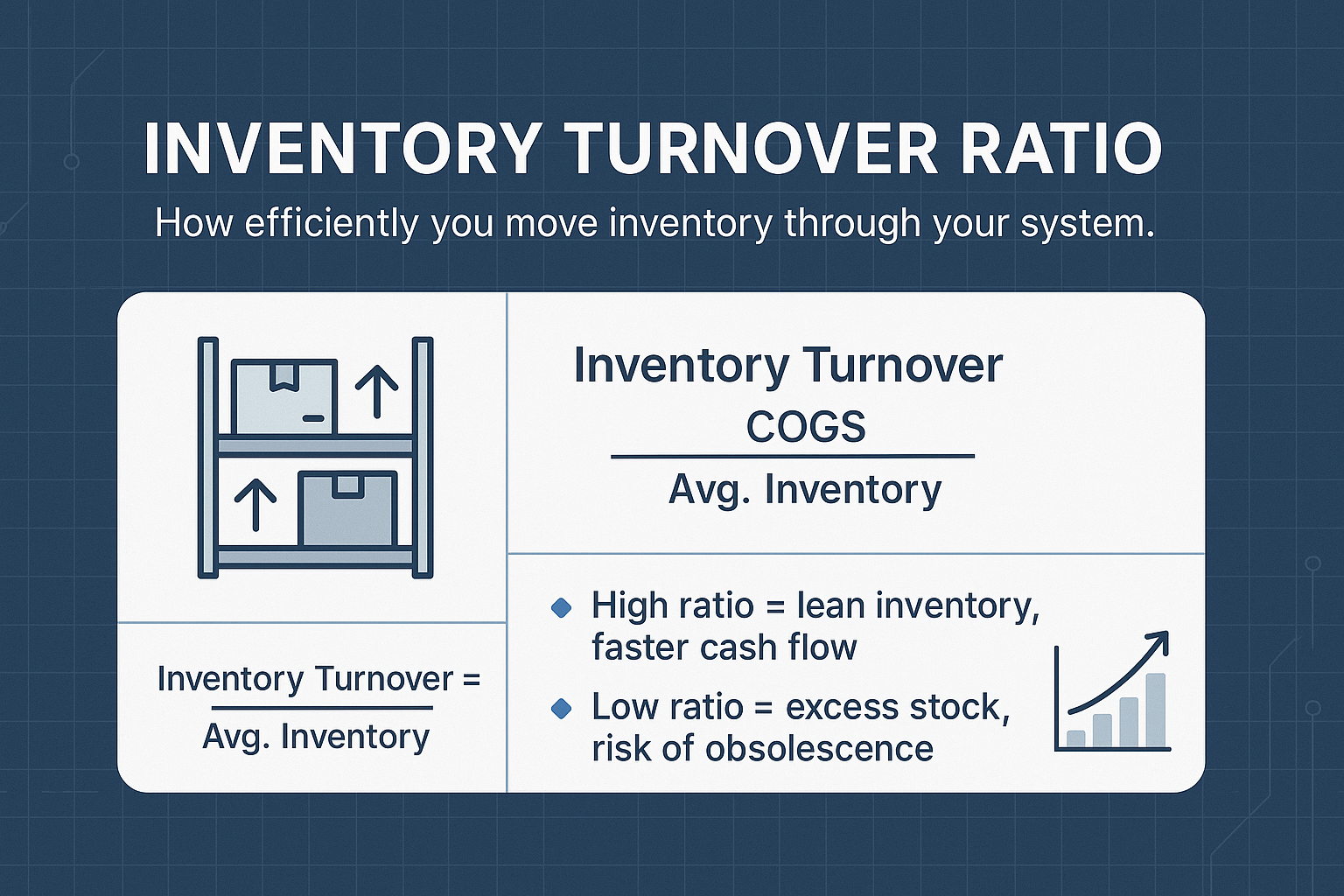
The Inventory Turnover Ratio is a vital KPI that indicates how quickly inventory is sold and replaced, providing insights into inventory management efficiency. A high inventory turnover ratio signifies efficient inventory management, while a low turnover rate suggests issues such as overstocking or low demand.
This key performance indicator is calculated by dividing the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) by the average inventory value, making it a critical metric for effective inventory management, optimizing inventory levels, and enhancing supply chain efficiency.
Cycle Time
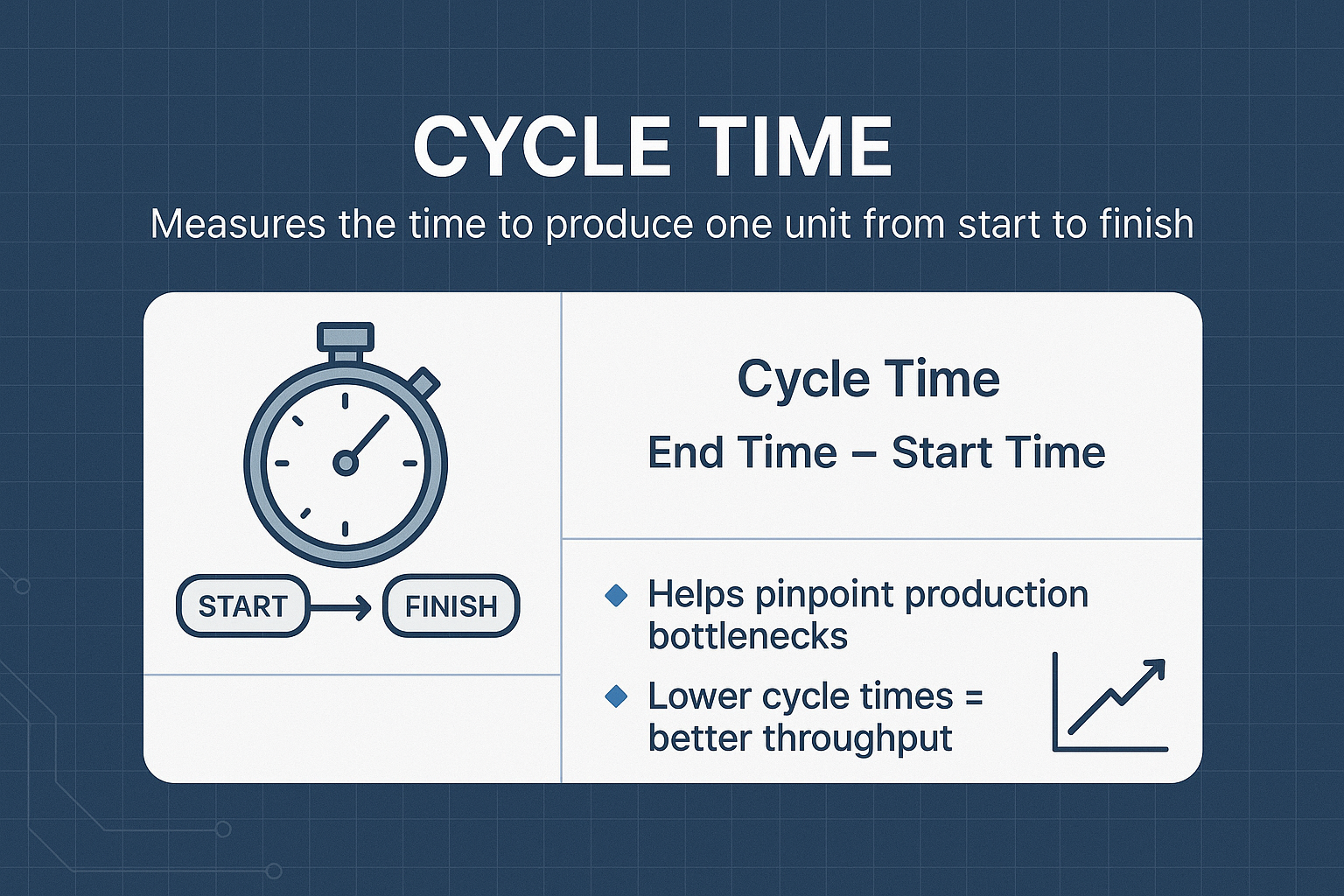
Cycle Time quantifies the total duration taken to complete a production process for a single unit, helping identify potential bottlenecks and areas for improvement. This KPI is calculated by subtracting the production start time from the production end time, offering a clear view of production efficiency and highlighting productivity issues. Additionally, understanding lead time, which measures the total time it takes to complete a production cycle from start to finish, provides a broader perspective on overall production timelines.
Monitoring and aiming to reduce Cycle Time enhances operational efficiency and helps meet production schedules more effectively.
Capacity Utilization
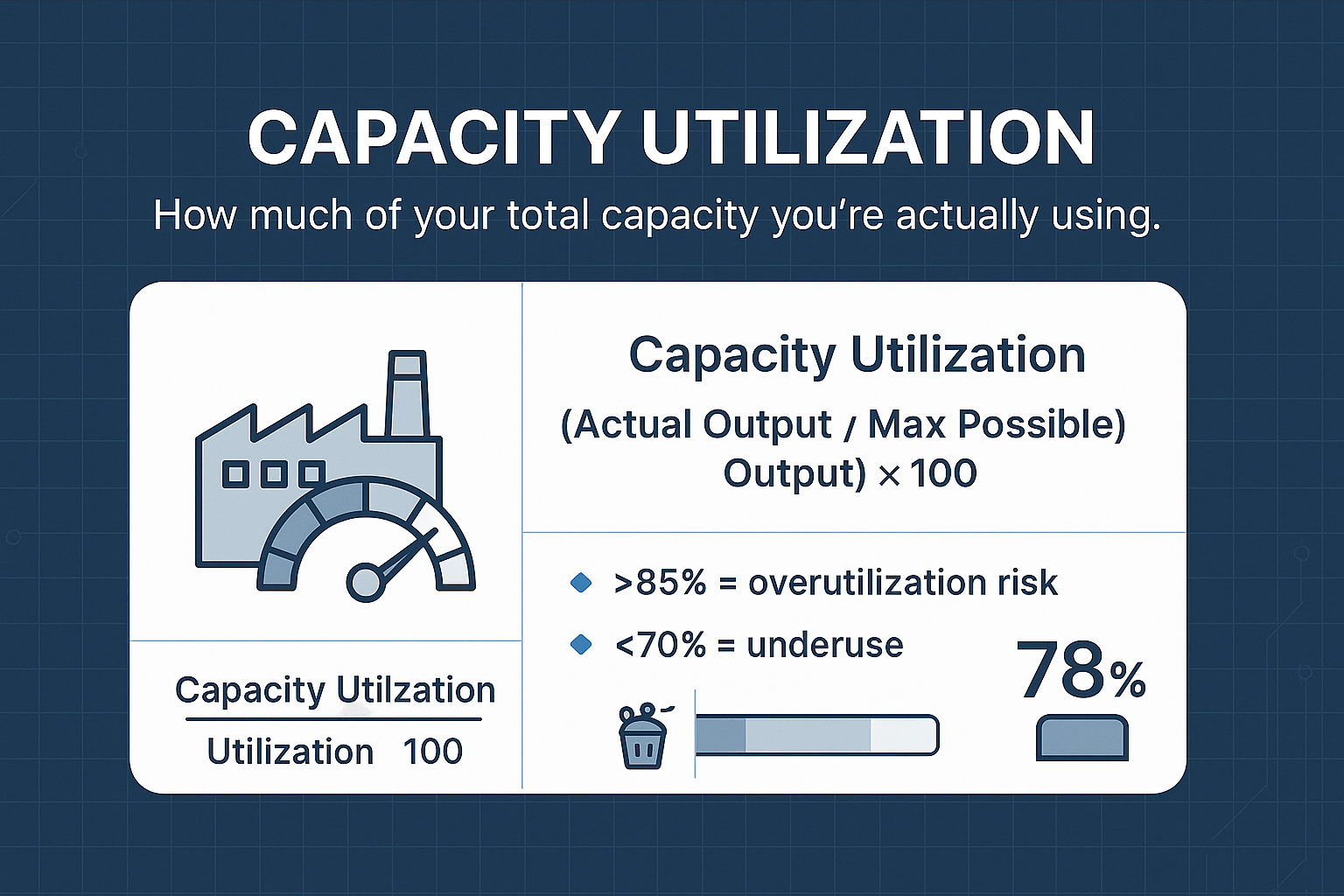
Capacity Utilization measures the percentage of actual production output compared to potential output, revealing the efficiency of production resources. This KPI is calculated using the formula: (Actual Output / Potential Output) * 100. A higher capacity utilization percentage indicates more effective use of production capacity, while a lower percentage suggests underused resources or inefficiencies.
Monitoring this metric helps manufacturers avoid overutilization risks and ensure optimal production efficiency.
Enhancing Production Efficiency with KPIs
KPIs are not just metrics; they are powerful tools for enhancing production efficiency. Tracking the right KPIs helps manufacturers identify inefficiencies and make informed strategic decisions to improve production processes. For instance, a decrease in the waste reduction rate signifies increased efficiency, contributing to cost savings and sustainability efforts. Advanced analytics can forecast demand trends, allowing proactive adjustments in production schedules and ensuring that production goals are consistently met.
Enhancing production efficiency involves continuously monitoring KPIs to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement in the manufacturing process. This approach enables manufacturers to optimize production processes, achieve cost efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
The following subsections will explore three key KPIs that are instrumental in enhancing production efficiency: On-Time Delivery Rate, Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), and Work-in-Progress (WIP).
On-Time Delivery Rate
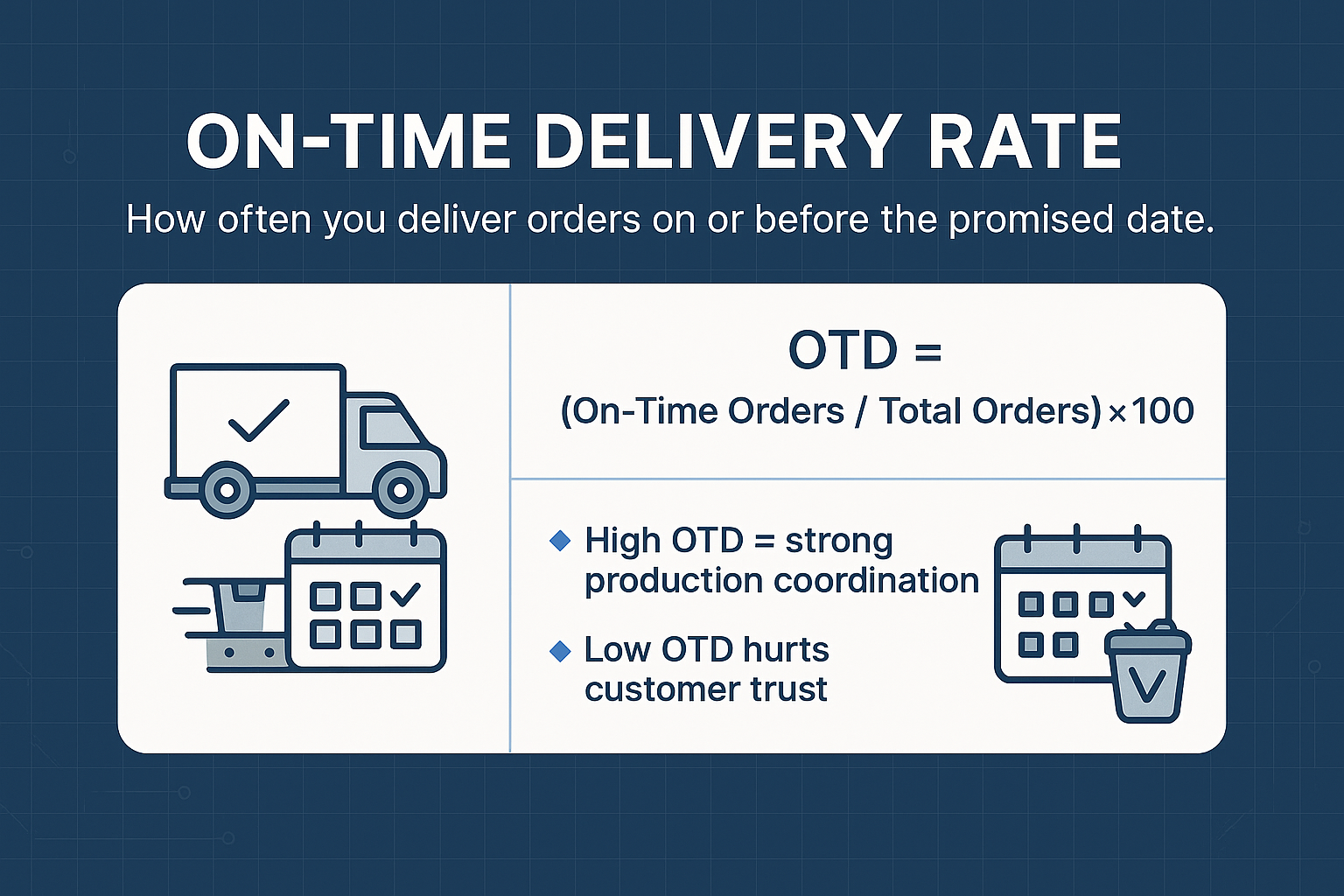
On-Time Delivery Rate (OTD) measures the ability to meet customer delivery expectations, which is crucial for retaining customers and enhancing overall satisfaction. This KPI is calculated as the percentage of orders delivered on or before the committed date. A low OTD rate may indicate production delays or poor resource allocation, affecting customer trust and retention. Closely related to this is order fulfillment time, which measures the time it takes for an order to be processed, manufactured, and delivered, providing further insights into the efficiency of the production and delivery process.
Analyzing and improving OTD rates helps manufacturers optimize production schedules and meet customer demands more effectively.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
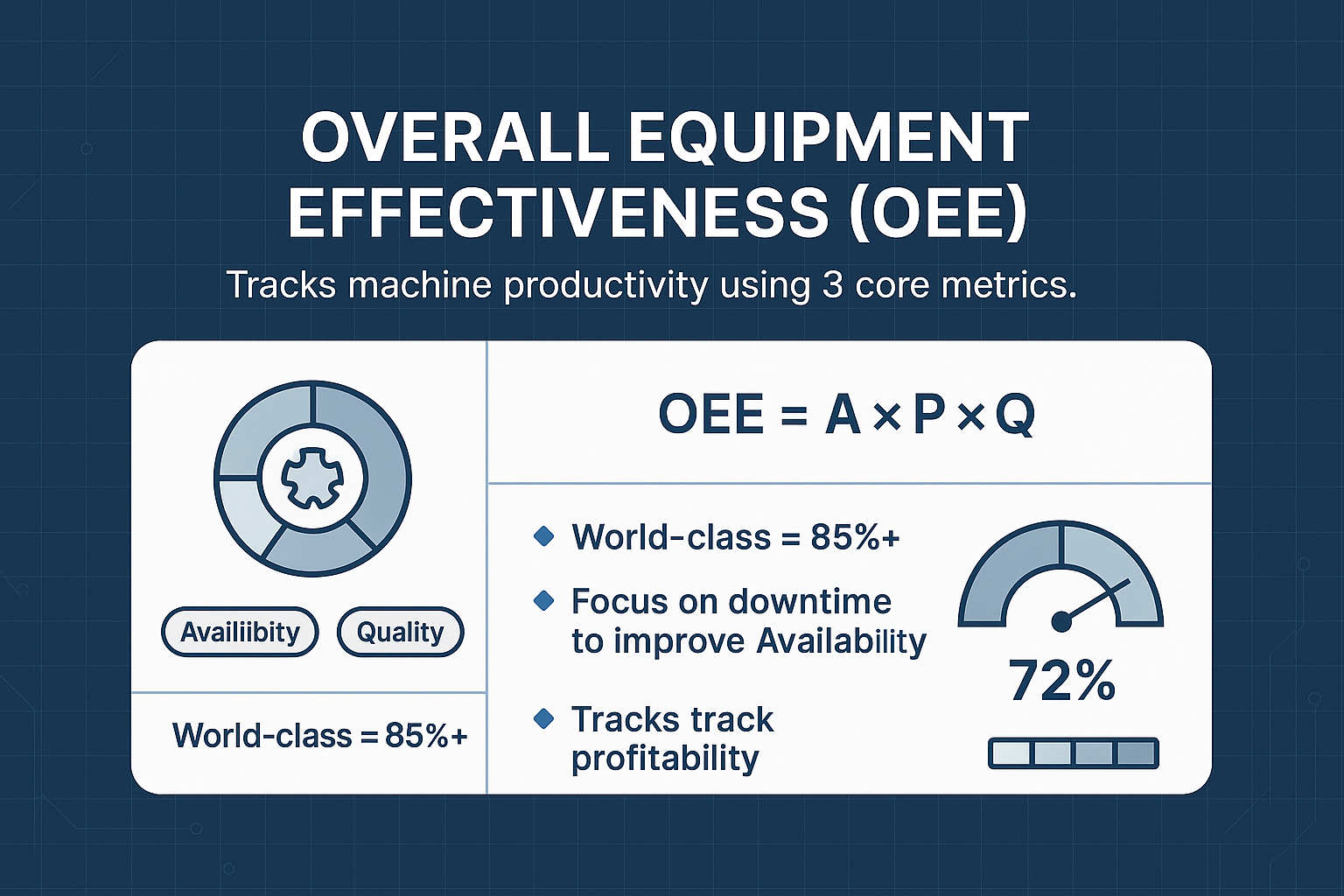
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) measures the productivity level of a machine or production platform by combining machine availability, performance, and output quality. A perfect OEE score is 100%, indicating optimal equipment effectiveness. Another critical metric to consider is the defect rate, which measures the percentage of products that are produced incorrectly and fail to meet quality standards. Monitoring this rate helps identify quality issues and improve production processes.
Scheduled maintenance is a key factor in maintaining high OEE, as it minimizes unplanned downtime and is often tracked through KPIs such as Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP) and Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF).
Implementing predictive maintenance can significantly decrease unexpected equipment failures, thereby improving OEE and ensuring smooth production operations. Enhancing OEE not only boosts production efficiency but also contributes to cost efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Work-in-Progress (WIP)
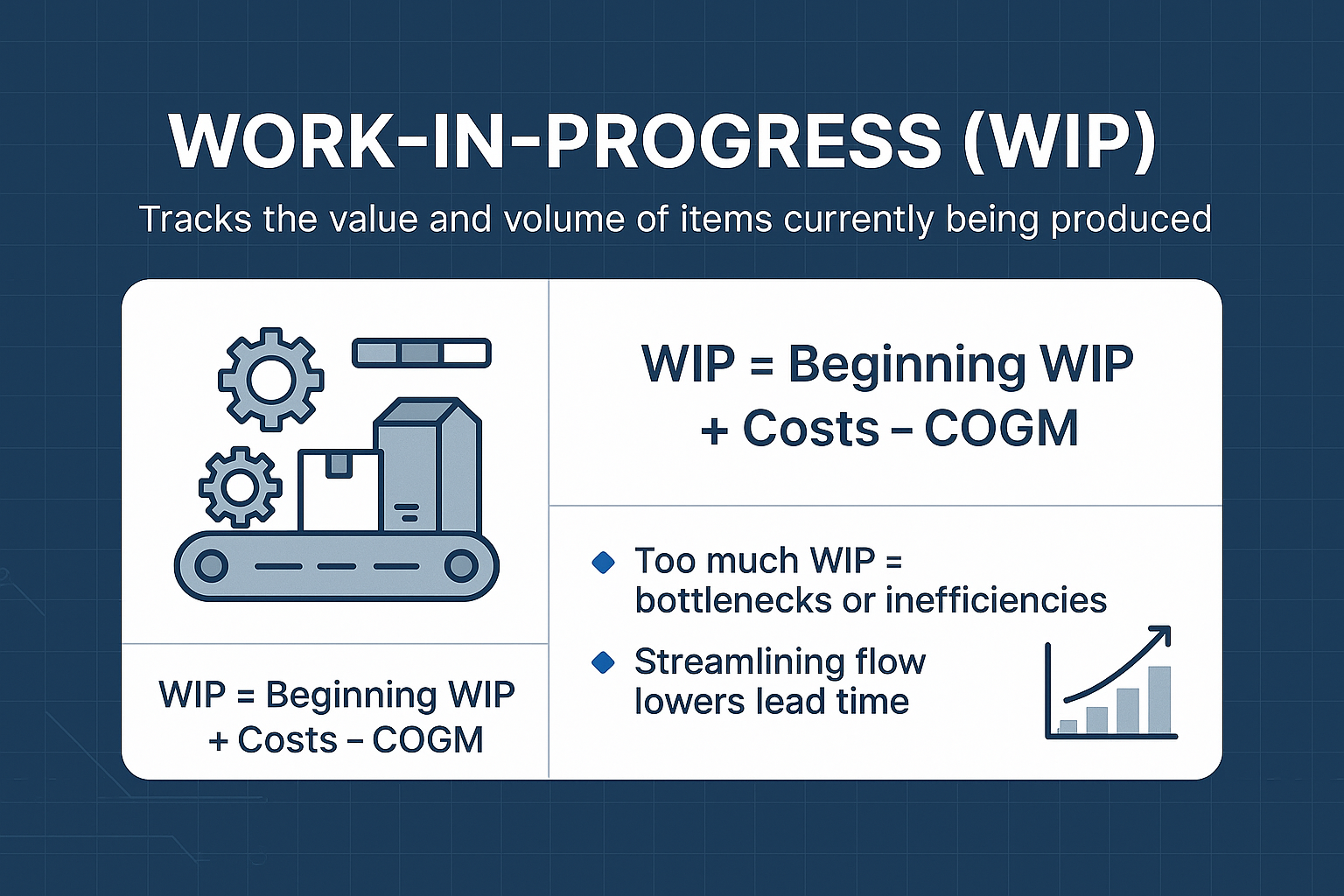
Work-in-Progress (WIP) measures the amount of unfinished work in the production process and estimates the value of products in production. Monitoring WIP helps identify inefficiencies, potential waste, or bottlenecks, ensuring a smooth workflow and continuous improvement.
This KPI is calculated using the formula: Beginning WIP + Manufacturing Costs – Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM). Keeping an eye on WIP levels is essential for effective production planning and operational efficiency.
Financial Impact of Production KPIs
Production KPIs have a profound financial impact on a company. By identifying cost-saving opportunities and enhancing profitability, these KPIs directly influence a company’s financial health. Monitoring cost metrics provides valuable insights into performance trends and areas for improvement, enabling data-driven decision-making. For instance, tracking Work-in-Progress (WIP) indicates the total value of materials and labor costs still in production, helping manufacturers control costs effectively. Minimizing lost production due to equipment downtime or process inefficiencies can lead to significant cost savings and enhance profitability, as tracking lost production helps justify investments in preventative maintenance and improve cost control.
Scenario modeling is another powerful tool that can identify the most cost-effective resource allocation across various production scenarios. This approach helps manufacturers balance costs, capacity, and delivery timelines, ultimately driving cost efficiency and ensuring overall business success.
The following subsections will delve into three key financial KPIs: Production Cost per Unit, Material Usage, and Waste Reduction Rate.
Production Cost per Unit
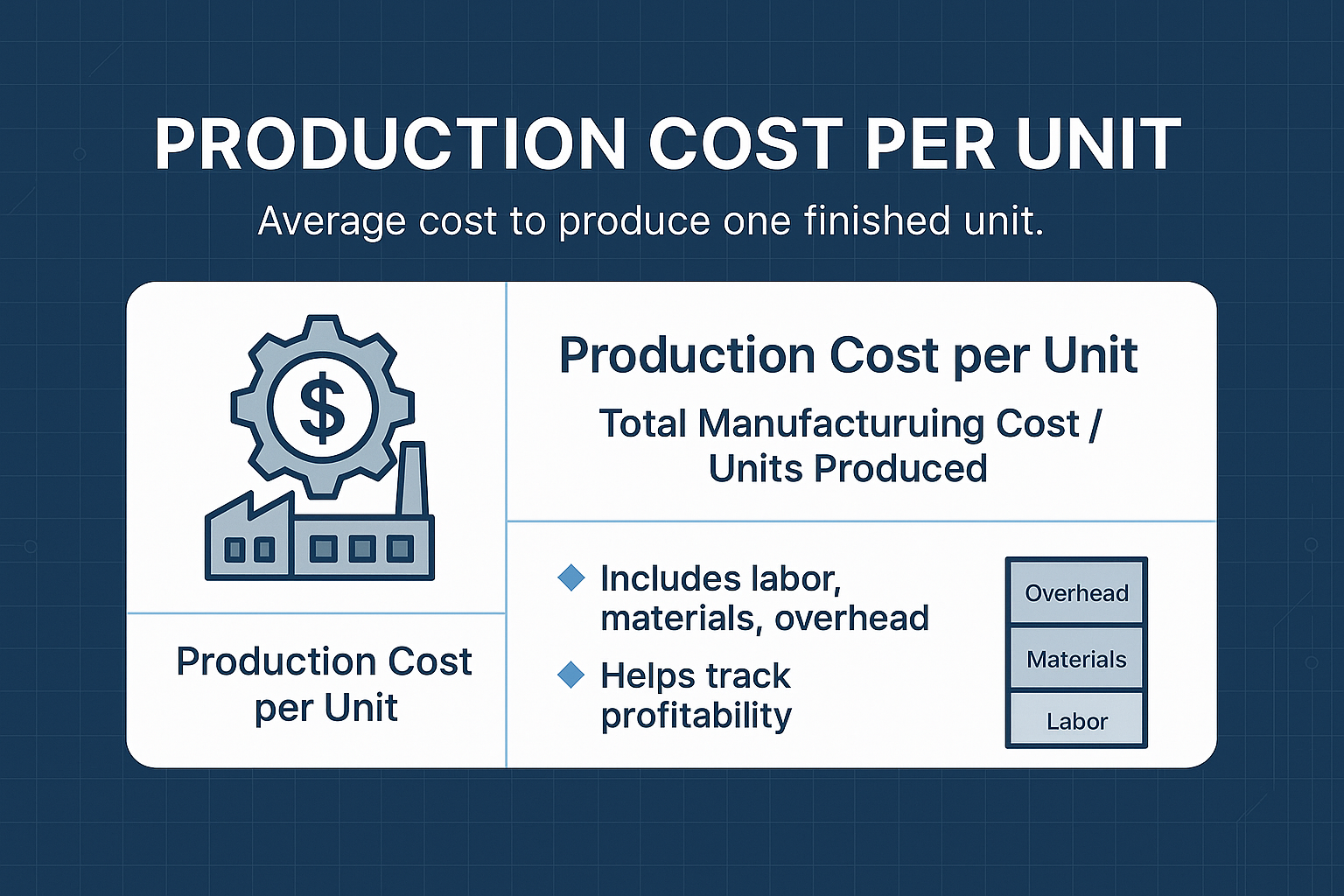
The Production Cost per Unit metric measures the average cost of producing one unit and is calculated by dividing the total manufacturing cost by the number of units produced. This KPI includes the total production cost of:
-
Materials
-
Infrastructure
-
Workforce costs
-
Overheads
-
Unit production cost
Tracking this metric is crucial for identifying cost-cutting opportunities, enhancing profitability, and ensuring that production remains cost-effective and competitive to reduce costs.
Material Usage
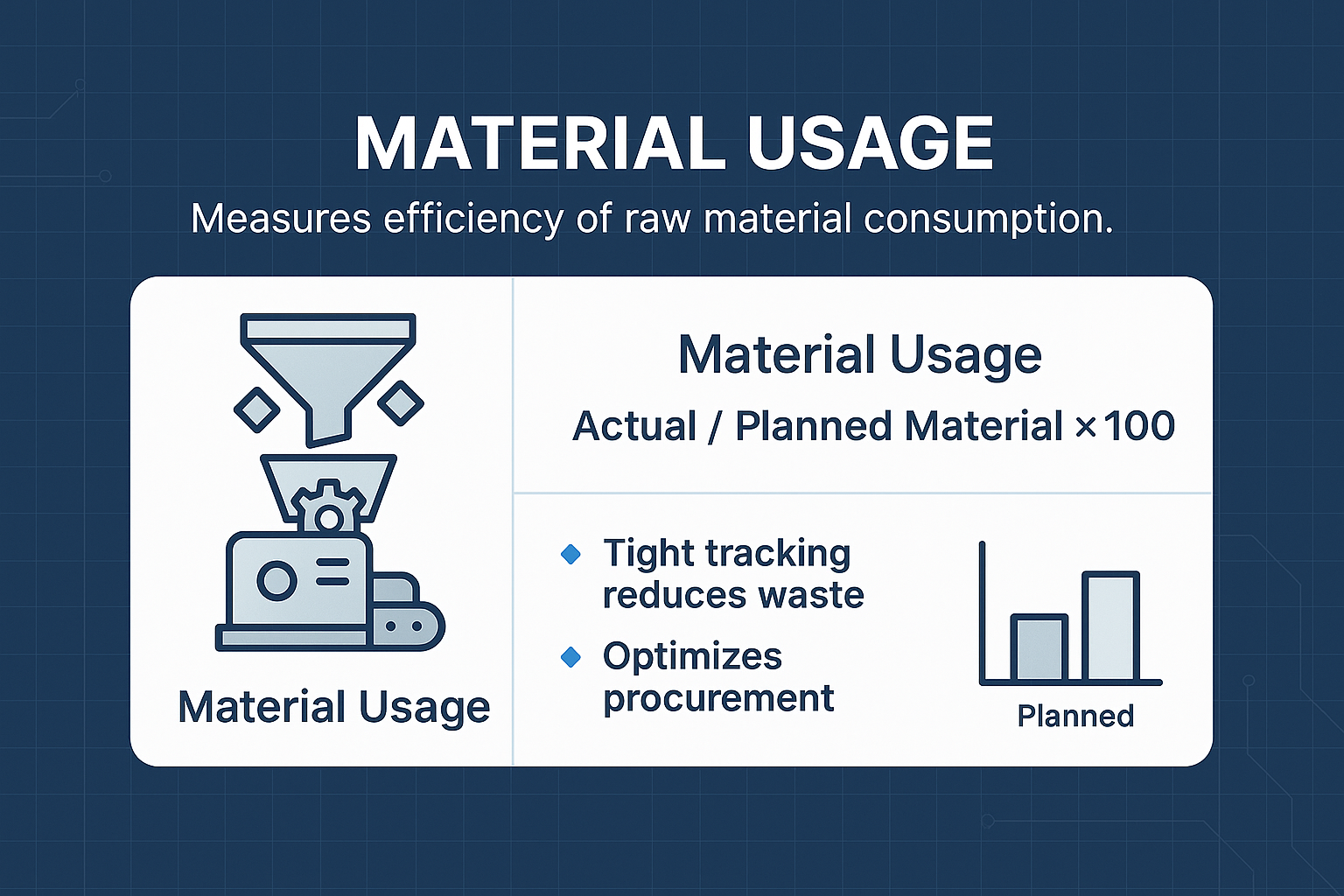
Material Usage evaluates actual versus planned material consumption, helping manufacturers minimize waste and control costs effectively. Closely monitoring this KPI ensures raw materials are used efficiently, reducing material costs and enhancing production efficiency. A high yield rate, which indicates effective production processes that minimize waste and maximize usable products, further complements material usage by ensuring that resources are utilized to their fullest potential.
This focus on material cost usage is critical for optimizing resource allocation and achieving cost efficiency in the production process.
Waste Reduction Rate

The Waste Reduction Rate measures the rate of reducing or increasing waste in production, with the goal of minimizing waste to improve production efficiency and sustainability. This KPI is calculated using the formula: Materials Used / Waste Material * 100, and is presented as a percentage. Similarly, the yield rate, which measures the percentage of products manufactured correctly and meeting quality standards, is a vital indicator of production efficiency. A high yield rate reflects effective processes that minimize waste and maximize usable products.
Setting specific goals for waste reduction, such as aiming to reduce waste by a certain percentage each quarter, can drive continuous improvement and cost savings.
Production Planning Tools and Techniques
To achieve operational excellence and meet business objectives, manufacturers rely on a variety of production planning tools and techniques. These resources are essential for monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cycle time, capacity utilization, and inventory turnover ratio, all of which provide valuable insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of production operations. Monitoring stockout rates also provides critical insights into maintaining optimal inventory levels, ensuring that production planning remains efficient and responsive to demand.
Modern production planning often leverages advanced software solutions, including enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, manufacturing execution systems (MES), and supply chain management platforms. These tools enable real-time tracking of production schedules, streamline communication across departments, and support data-driven decision making. By integrating these systems, manufacturers can optimize production processes, reduce production costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
In addition to digital tools, proven methodologies like lean manufacturing, total productive maintenance (TPM), and six sigma are widely used to minimize waste, enhance quality, and boost productivity. These techniques help manufacturers identify inefficiencies, standardize best practices, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
By combining robust tools with effective techniques, manufacturers can optimize production schedules, improve capacity utilization, and ensure that production planning aligns with business objectives. This integrated approach delivers valuable insights, supports efficient inventory management, and ultimately drives better outcomes for both the business and its customers.
Leveraging Technology for KPI Tracking
In the age of digital transformation, leveraging technology for KPI tracking is essential for effective production planning. Key aspects include:
-
Data collection tools that gather real-time information from different production stages, greatly improving decision-making.
-
KPI dashboards that display real-time performance metrics, transforming raw data into usable insights.
-
The ability for manufacturers to monitor trends and make timely adjustments to production plans.
-
Traditional tracking methods, such as Excel spreadsheets, which are often inefficient due to manual data entry and make real-time insights difficult to obtain.
These enhancements can lead to more informed and effective choices.
Integrating advanced technologies into production planning allows for seamless data synchronization and predictive maintenance. These technologies not only improve production efficiency but also contribute to cost efficiency and overall business success.
The following subsections will explore three key technological advancements in KPI tracking: Real-Time Data Synchronization, Predictive Maintenance Integration, and Scenario Planning and Optimization.
Real-Time Data Synchronization
Real-Time Data Synchronization involves:
-
Seamless integration of production planning software with enterprise systems like SAP, Oracle, or Microsoft Dynamics
-
Automatic data collection
-
Real-time monitoring of KPIs
-
Optimizing production schedules
Leveraging real-time data helps manufacturing companies enhance on-time delivery rates and make informed decisions to improve production efficiency.
Predictive Maintenance Integration
Predictive Maintenance Integration uses data analytics and machine learning to anticipate equipment failures before they occur. Regular monitoring of equipment performance through predictive maintenance ensures machinery operates optimally, reduces unplanned downtime, and maintains efficient production schedules.
This proactive approach to schedule maintenance proactively enhances overall reliability and production efficiency.
Scenario Planning and Optimization
Scenario Planning and Optimization involves evaluating multiple scheduling scenarios to find the optimal balance between production costs and capacity utilization. By leveraging data from predictive maintenance, manufacturers can schedule maintenance during non-peak hours, optimize operations and enhance operational efficiency.
This approach helps to identify areas for improvement and ensures that production goals are met cost-effectively.
Achieving a Competitive Edge
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing industry, gaining a competitive edge requires more than just meeting production targets—it demands continuous optimization of production processes and a commitment to operational excellence. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), capacity utilization, and inventory turnover ratio are instrumental in identifying areas for improvement and driving superior production performance.
Manufacturers who prioritize efficient inventory management, reduce production costs, and consistently deliver on time are better positioned to enhance customer satisfaction and build lasting relationships. Effective production planning, supported by real-time KPI tracking, enables companies to quickly adapt to changing market conditions and customer expectations.
Investing in advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT) further strengthens a manufacturer’s ability to optimize production efficiency, minimize waste, and increase productivity. These innovations provide deeper insights into production operations, allowing for proactive decision making and continuous improvement.
By leveraging these strategies and tools, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement, streamline production operations, and maintain a competitive edge. This not only leads to increased market share and revenue but also ensures long-term business success in an ever-evolving manufacturing landscape.
Production Planning and Industry Trends
The landscape of production planning is constantly evolving, shaped by emerging industry trends, shifting customer demands, and rapid technological advancements. Staying ahead requires manufacturers to closely monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as demand forecasts, inventory levels, and supply chain efficiency, all of which are critical for adapting to market changes and optimizing production processes.
The rise of e-commerce and the demand for faster, more flexible production have made agile production planning more important than ever. Manufacturers are increasingly leveraging AI and machine learning to enhance predictive maintenance, optimize production schedules, and improve overall production efficiency. These technologies enable real-time analysis of production data, helping companies respond quickly to fluctuations in customer demands and market conditions.
Additionally, global supply chain shifts and sustainability initiatives are influencing how manufacturers approach inventory management and production costs. By tracking relevant KPIs and staying informed about industry trends, manufacturers can identify opportunities to optimize production processes, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Incorporating industry trends into production planning not only ensures operational agility but also positions manufacturers to capitalize on new opportunities and maintain a strong competitive position in the marketplace.
Best Practices for Implementing Production KPIs
To implement production KPIs effectively, consider the following:
-
Use a systematic approach.
-
Ensure continuous optimization for success.
-
Implement accurate data collection systems to provide reliable insights and ensure effective KPI tracking.
-
Continuously track KPIs and adjust based on real-time insights to monitor and adjust production schedules effectively.
-
Start with the right KPIs and integrated technology for successful production planning.
Collaborating across procurement, sales, and maintenance teams ensures alignment of schedules and resources during production. Investing in training to leverage integrated tools effectively in production planning is also important.
Embracing a culture of continuous improvement enables manufacturers to use KPI results to drive corrective actions and enhance overall performance. The following subsections will explore best practices for accurate data collection, regular performance reviews, and continuous improvement.
Accurate Data Collection
Accurate data collection is crucial for the reliability and effectiveness of KPI tracking. Establishing a KPI monitoring system requires accurate and timely data capture to provide valuable insights. Common pitfalls include tracking too many KPIs, which can dilute focus.
Team training is essential for educating staff on how to track and interpret KPIs effectively. Regularly analyzing collected data helps spot performance trends and identify areas needing improvement.
Regular Performance Reviews
Regular performance reviews of KPIs are essential for ensuring ongoing production efficiency and meeting business objectives. Involving relevant stakeholders in the monitoring and reporting process fosters a collaborative environment, leading to better identification of performance gaps.
Identifying gaps through regular reviews allows for the implementation of targeted improvement plans, driving continuous production enhancement.
Continuous Improvement
Embracing a culture of continuous improvement requires:
-
Utilizing KPI results to drive initiatives and implement corrective actions.
-
Setting realistic targets to ensure KPIs align with current capabilities and resources.
-
Regularly evaluating the effectiveness of improvement efforts.
-
Adjusting strategies as needed for ongoing optimization.
This approach not only enhances production efficiency but also ensures overall business success and a competitive edge.
Summary
Mastering production planning KPIs is crucial for achieving manufacturing efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. By understanding and implementing key metrics such as Inventory Turnover Ratio, Cycle Time, Capacity Utilization, and others, manufacturers can optimize production processes and align them with business objectives. Leveraging technology for real-time data synchronization and predictive maintenance further enhances KPI tracking and decision-making capabilities. Embracing best practices like accurate data collection, regular performance reviews, and continuous improvement ensures that production goals are met effectively and efficiently. With the right KPIs and strategies in place, manufacturers can achieve overall business success and maintain a competitive edge.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are production planning KPIs?
Production planning KPIs are essential metrics that assess efficiency, quality, and resource utilization in the production process, enabling manufacturers to effectively meet their production goals. These indicators provide valuable insights for continuous improvement in manufacturing operations.
How do KPIs enhance production efficiency?
KPIs enhance production efficiency by pinpointing bottlenecks and guiding strategic decisions, which leads to optimized processes and cost reduction. This ultimately enables organizations to improve their overall operational performance.
What is the importance of Inventory Turnover Ratio in production planning?
The Inventory Turnover Ratio is crucial in production planning as it reflects the efficiency of inventory management and reveals how quickly products are sold and replaced. This insight aids manufacturers in optimizing inventory levels and enhancing supply chain efficiency.
How does Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) impact production?
Improving Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) significantly enhances production by ensuring smoother operations, increasing cost efficiency, and boosting customer satisfaction through higher quality output. Therefore, focusing on OEE is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes.
Why is accurate data collection important for KPI tracking?
Accurate data collection is essential for reliable insights and effective KPI tracking, enabling timely adjustments and informed decisions to enhance production efficiency. Without precise data, performance assessments may be flawed, leading to suboptimal outcomes.
What is KPIs in planning?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in planning refer to measurable values that organizations use to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of their planning processes. In production planning, KPIs help track how well the production schedules, resource allocation, and inventory management align with business goals. These indicators provide actionable insights that enable manufacturers to optimize operations, reduce costs, and meet customer demands reliably.
What is the KPI for a production manager?
A production manager focuses on KPIs that reflect the overall performance of the manufacturing process. Key KPIs for a production manager typically include:
-
On-Time Delivery Rate: Measures the percentage of orders delivered on schedule, ensuring customer satisfaction.
-
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): Combines machine availability, performance, and quality to assess equipment productivity.
-
Production Cost per Unit: Tracks the average cost incurred to produce one unit, helping manage budgets and pricing.
-
Cycle Time: Indicates the duration to complete one production cycle, highlighting efficiency.
-
Defect Rate: Measures the percentage of products failing quality standards, guiding quality improvement efforts.
Monitoring these KPIs helps production managers maintain operational efficiency, control costs, and ensure product quality.
What are the 5 steps in production planning?
Effective production planning generally follows these five key steps:
-
Forecasting Demand: Estimating customer demand to determine production requirements.
-
Capacity Planning: Assessing available resources, including machinery and labor, to meet production goals.
-
Scheduling Production: Creating detailed production schedules to optimize workflow and meet deadlines.
-
Inventory Management: Ensuring the right amount of raw materials and components are available to avoid stockouts or overstocking.
-
Monitoring and Controlling: Tracking production progress through KPIs and making adjustments to address bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
Following these steps helps manufacturers align production with business objectives and maintain smooth operations.
What are the 5 KPIs that are used to track performance?
Five essential KPIs commonly used to track production performance include:
-
Inventory Turnover Ratio: Reflects how quickly inventory is sold and replenished, indicating inventory management efficiency.
-
Cycle Time: Measures the time taken to produce a single unit, highlighting process efficiency.
-
Capacity Utilization: Shows the extent to which production capacity is used, indicating resource optimization.
-
On-Time Delivery Rate: Tracks the percentage of orders delivered as promised, reflecting customer satisfaction.
-
Defect Rate: Assesses product quality by measuring the percentage of defective units produced.
These KPIs provide a comprehensive view of production effectiveness, quality, and customer service.
What is KPI in production planning?
In production planning, a KPI (Key Performance Indicator) is a quantifiable metric used to evaluate how well the production process meets its objectives. These KPIs help manufacturers monitor aspects such as efficiency, quality, cost control, and delivery performance. By regularly tracking KPIs, production planners can
Share this
You May Also Like
These Related Stories
.png)
How to Make a Production Schedule for Manufacturing

Top 15 Key Performance Indicators in Manufacturing Industry to Monitor


No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think